
| Parasite | Haemobaphes diceraus (= Haemobaphes theragrae) |
|---|---|
| Taxonomy | Arthropoda, Crustacea, Copopoda |
| Hosts | Alaska pollack (Theragra chalcogramma), Pacific cod (Gadus macrocephalus), littlemouth flounder (Pleuronectes herzensteini) |
| Infection site | Gill (to the bulbus arteriosus) |
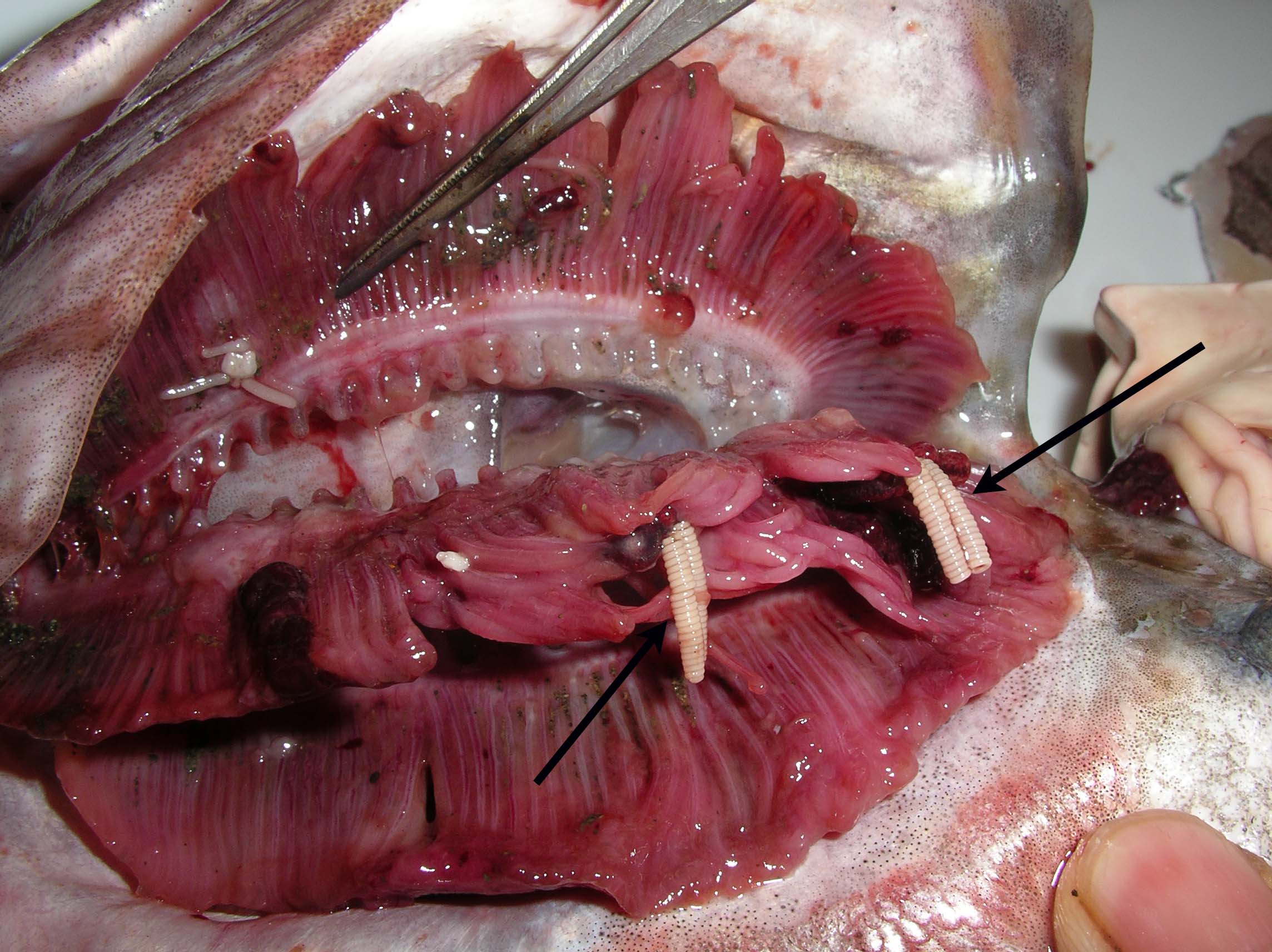
| Clinical sign | A parasite (over 1 cm) is visually observed in the gill filament (Fig. 1). |
| Parasitology | The parasite has an elongated neck extending through the gill arch and the abdominal aorta directly into the bulbus arteriosus (Fig. 2). It feeds on hostfs blood. |
| Pathology | Haemobaphes diceraus possibly influences the reproduction of the host by adverse effects on the nutritional condition (Katakura et al., 2004). |
| Health hazard | Since this parasite is not infectious to human, it is harmless in food hygiene. |
| Diagnosis | Check the parasite in the gill filament. H. diceraus can be readily differentiated from Clavella perfida parasitizing the gill of Alaska pollack since the latter is smaller and has no long necks. |
| Other information | Emaciated Alaska pollack with pale anaemic gills has been found in the eastern Hokkaido. Katakura et al. (2004) suggested that this is caused by Haemobaphes diceraus. Though H. diceraus was separately described from H. theragrae according to Kabata (1988), Katakura et al. (2004) considered to be the identical species, followed by Ho and Kim (1996). |
| References | Ho, J. S. and I. H.
Kim (1996): Copepods parasitic on fishes of western north pacific. Publ. Seto. Mar. Biol. Lab., 37, 275-303. Kabata, Z. (1988): Copepoda and Branchiura. Guide to the parasites of fishes of Canada. Part II-Crastacea. In: Margolis, L. and Z. Kabata (eds) Can. Spec. Publ. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 101, 3-127. Katakura, S., Y. Sakurai, H. Yoshida, A. Nishimura, K. Konishi and T. Nishiyama (2004): Influence of the parasitic copepod Haemobaphes diceraus and Clavella perfida on growth and maturity of walleye pollock Theragra chalcogramma. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 70, 324-332. (In Japanese) |
Fig. 1. Haemobaphes (arrows) on the gill of Alaska pollack.
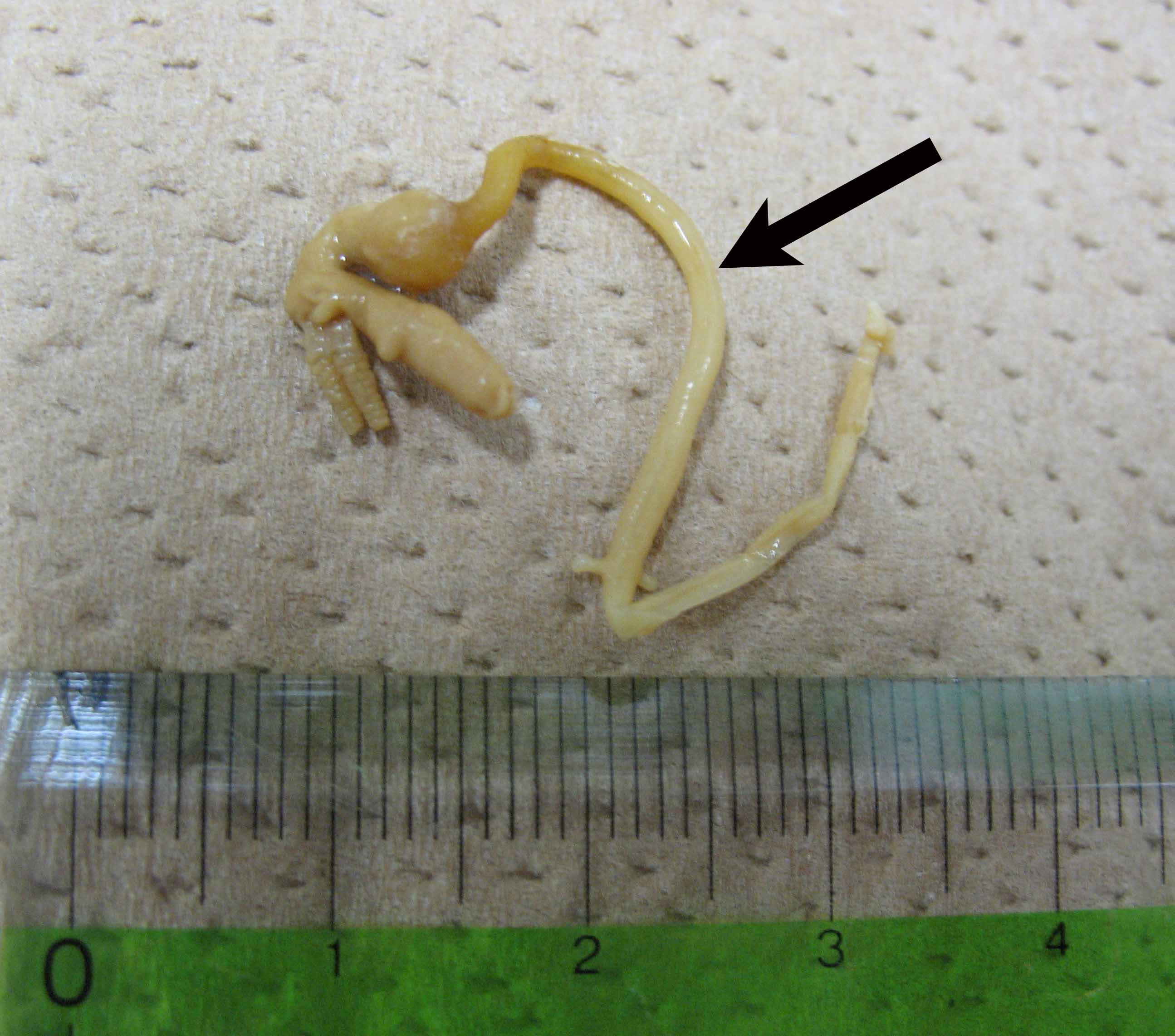
Fig. 2. Haemobaphes collected from the fish. Arrow shows the neck
extending to the bulbus arteriosus.